In our everyday lives, we are exposed to numerous types of sounds. It could be as quiet as the leaves in a forest, a conversation, or loud as a machine in a factory. Loud sounds can damage your hearing permanently so you should take measures to prevent this. An environment with higher decibels (dB) can be dangerous. Sound can be measured in two ways. The frequency is measured in Herts (Hz), and intensity can be measured in decibels (dB). In this article, we will dive into why hearing protection is important.
How does the ear work?
Sound waves enter your outer ear then make their way through your ear canal to your eardrum. The sound waves will then cause your eardrum to vibrate causing the bones in your middle ear to move. The movement of these bones causes the fluid in your inner ear section to move. This movement of fluid then causes hair cells in your cochlea to move. Your hair cells’ movement is then produced into electrical pulses, sent to your auditory nerve and to your brain. Your brain will then interpret this as sound.
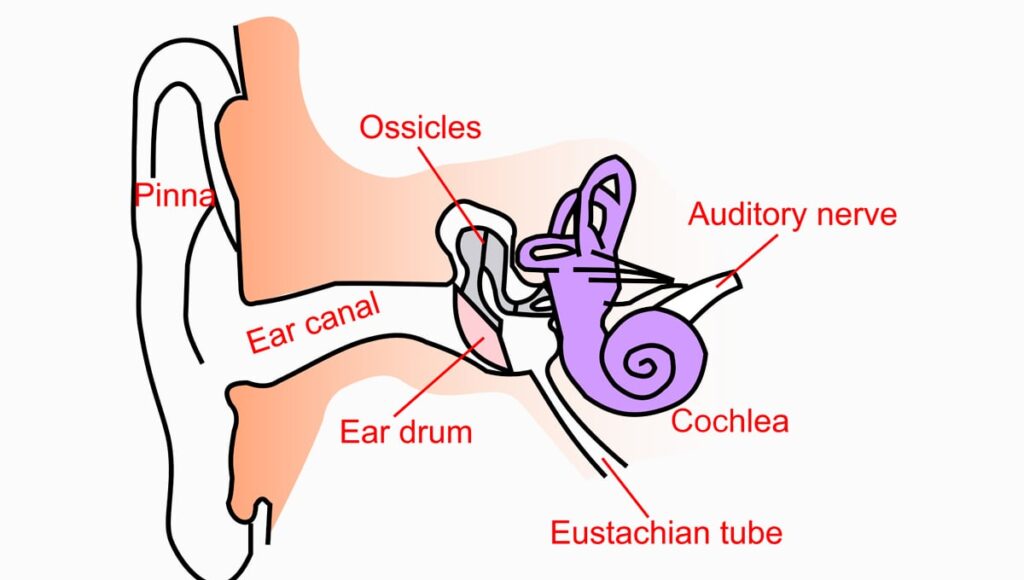
What causes hearing loss?
Hearing loss is commonly caused by the loss of hair cells in your inner ear. Loud noises are the reason why hair cells tend to get damaged or go missing. Other reasons why hearing loss occurs can be ear infections, earwax buildup, or a ruptured eardrum. A ruptured eardrum can occur when a foreign object enters your ear and damages your eardrum. It can also happen when there is a sudden change in pressure, a very loud noise, or an infection.
Prevention
The best method for preventing hearing loss is to prevent loud sounds if you can. Sometimes you can’t control the sound in your environment but you can control how much sound you are exposed to. For example, you can still prevent hearing loss by using PPE. PPE stands for Personal Protective Equipment. Earmuffs, earplugs, and semi insert earplugs are all forms of PPE. They also come in different styles, ratings, and pros/cons. Using hearing protection can prevent hearing loss. Most people lose the ability to hear high frequency sounds first, it might be hard to notice at first but hearing loss can develop to a point where conversations are hard to hear.
Myths
There are some common myths about hearing loss that need to be addressed. If you were to follow these myths it could definitely lead to hearing loss.
Questions
- Could you build up a resistance to loud noise?
- Can noise damage your hearing even if it’s not painful or loud?
- Could short loud noise really cause hearing damage?
- Can you recover your hearing if you already have lost a bit?
- Can you restore hearing with hearing aids?
Answers
- There is no way to build up resistance to loud noises. Even if you build up earwax it is still impossible.
- Noise can still damage you even if not painfully loud, 85dB is when hazard starts and 140dB is when the pain starts.
- Short loud noises are just as similar to continuos exposure to a lower hazardous sound for extended periods of time.
- Your hearing will never recover unless you are suffering from temporary hearing loss. Causes of temporary hearing loss can be middle ear infections, blocked ear canals, head trauma, swimmers ears, ototoxic medication, and loud noises depending on the situation.
- You can’t restore hearing 100% with hearing aids. It might help with conversations but there will be things you can’t hear.
Types of hearing protection
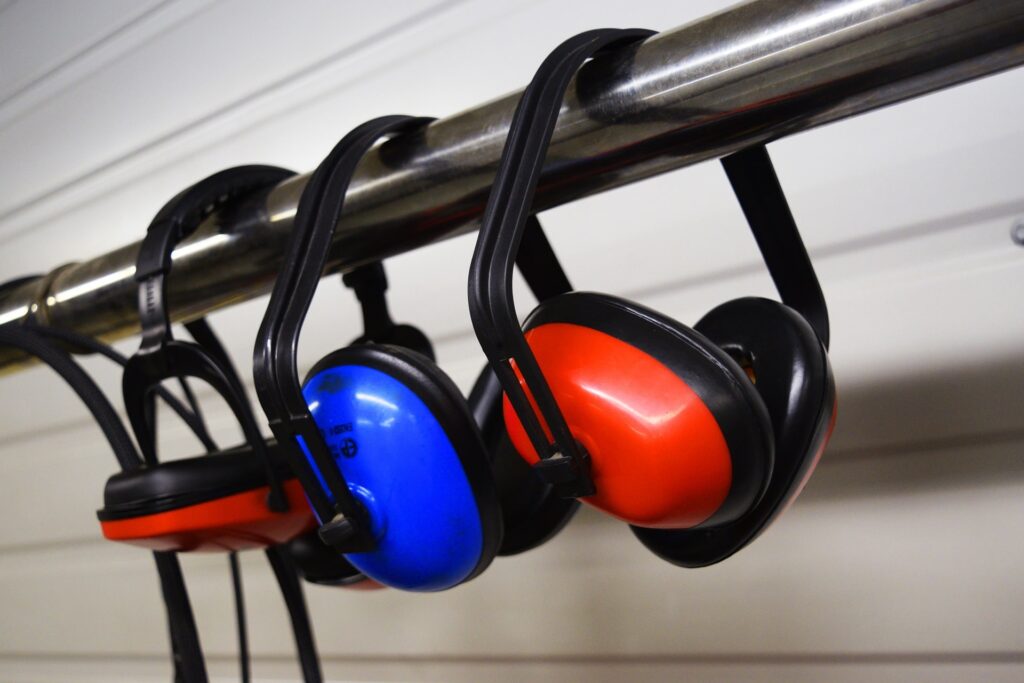
Earmuffs hearing protection
Earmuffs are an excellent choice for hearing protection. They can be adjusted to your preference. To wear earmuffs properly you must make sure there is a seal around your ear. Sometimes wearing safety glasses can break this seal but is inevitable. It can be uncomfortable in a humid environment but most people adapt to the feeling.
You can also get earmuffs that have electronic hearing protection, a great feature so you can hear quiet noises like a conversation but be protected from loud noises.

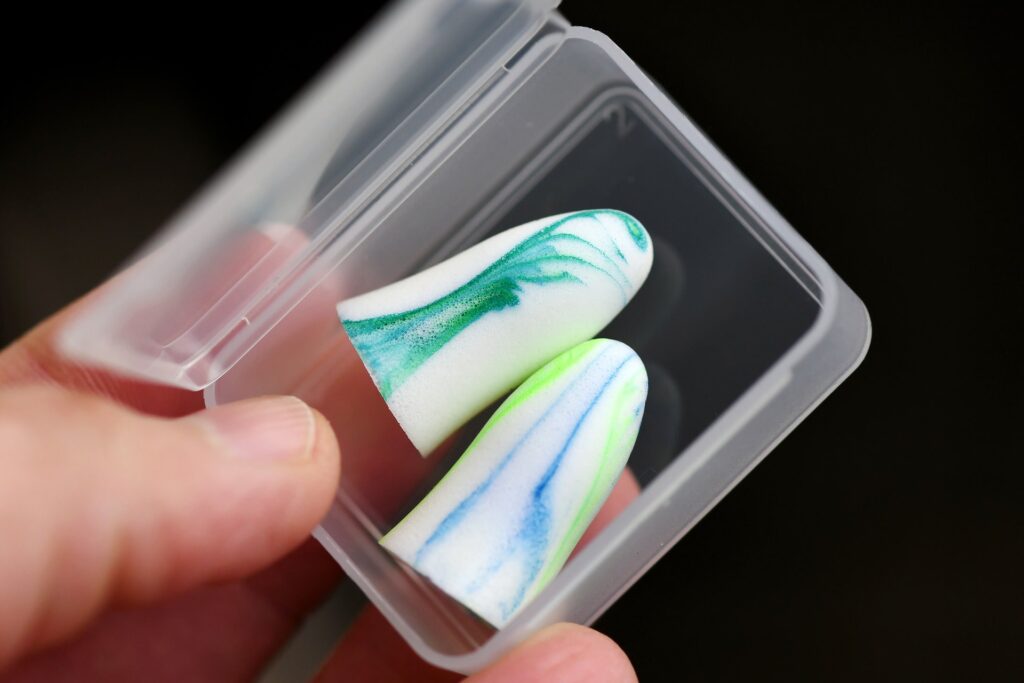
Earplugs hearing protection
Earplugs come in various styles. There are the common ones that are rolled and inserted into your ear canal. They will then expand in your ear canal and block the noise. The downside to them is there is no adjustment. If you remove them they are considered disposable.
Another style of earplugs is the push-in style. These earplugs just push into your ear canal and can be reused depending on the material of the earplug.
You can also get custom moulded earplugs, even with the option of electronic earplugs.

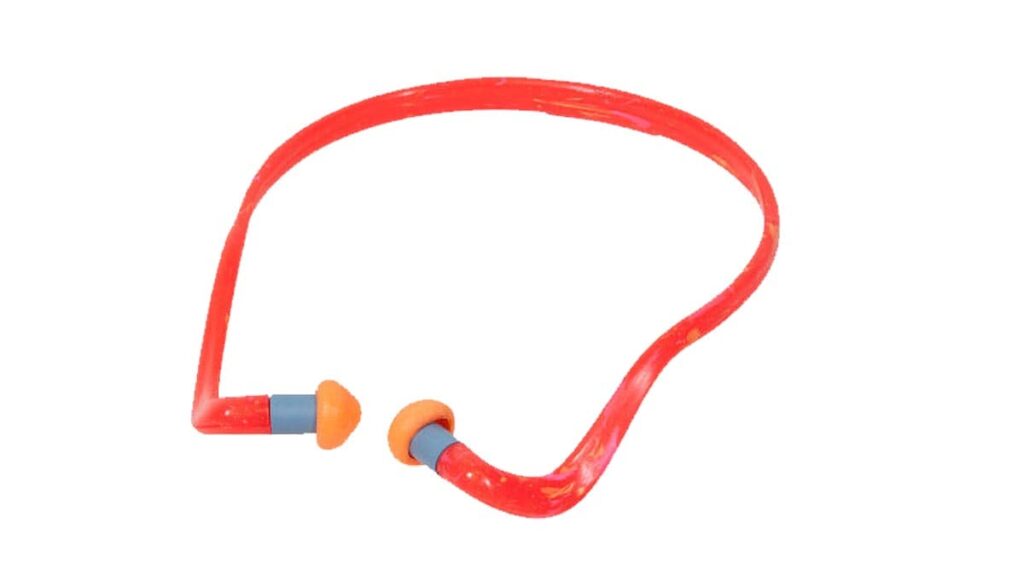
Semi-insert earplugs hearing protection
Semi-insert earplugs are similar to earplugs but they don’t fully insert into your ear canal like regular earplugs. These ones are on a rigid headband and are easy to use. The disadvantage to these is they typically don’t have the best NRR rating and can be more expensive than earplugs.

What is NRR?
NRR stands for Noise Reduction Rating. This value is how much decibels a hearing protection device will reduce in an environment. For example, if you were in an environment that averages 91dB, a hearing protection device rated at an NRR of 24dB would mean you are only exposed to 67dB. So the higher the NRR rating the more decibels a hearing protection device can protect you from.
Exposure risks
- 70dB no risk of damage
- 85dB your hearing is at risk after 8 hours of exposure
- 91dB your hearing is at risk after 2 hours of exposure
- 100dB your hearing is at risk after 15 Mins
- 115dB your hearing is at risk within 1 minute
- 140dB immediate hearing damage and pain is possible
Example of noises
- 0-10db = faint sounds like leaves
- 30dB = Quite whisper
- 50-60db = conversation sounds
- 80dB = Vacuum cleaner
- 100db = chainsaw machinery
- 120-130db = rock and roll band concert
- 150dB = 747 jet at full throttle
- 180db = space shuttle taking off
Conclusion
You should now understand how your hearing works and what can damage it. Most hearing loss in the workplace is preventable with hearing protection devices. As you now know a hazardous noise for 8 hours can put your hearing at risk. Most workplaces have 8-hour shifts and workers can be exposed to hazardous noise. Some people won’t notice the hearing loss until the end of their career, but at that point, the damage has been done and irreversible. This is why it is very important to prevent rather than react. If you are working around loud machinery or tools, make sure to use hearing protection devices.





